

This is no different from open inguinal hernia surgery as both procedures depend upon the natural body healing process to grow over the hernia mesh in order to return to normal strength.






Inguinal hernia surgery can be done by an urologist or general surgeon. Our urology centre practices the Totally Extraperitoneal (TEPP) approach,
which is the one of the latest and favored laparoscopy hernia surgery technique today. In this method, the inguinal hernia is
accessed without reaching the abdomen cavity (pre-peritoneal space) and the mesh is fixed to cover the weakened area. TEPP decreases
the risk of damage to internal organs and vascular injuries.
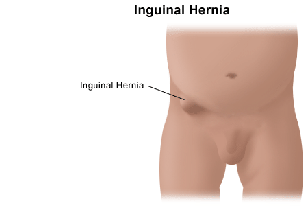
Surgical repair of inguinal hernia using mesh, which is a thin, plastic sheet, is the procedure of choice worldwide. Mesh can be inserted
by conventional (open) or laparoscopy (key-hole) surgery. Laparoscopy hernia surgery is preferred over open surgery where inguinal
hernia occur on both sides of the body or in recurrent inguinal hernia after a previous repair. Patients with inguinal hernia
on one side of the body should also consider a laparoscopy hernia surgery as it has significant advantages such as less post-operative
pain, earlier return to normal life and lower incidence of chronic pain.
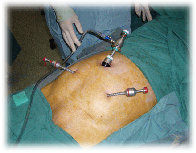
Laparoscopy surgery, often referred to as “keyhole” surgery, is a method of carrying out an operation without having to make a large
incision. Small cuts (between 5mm - 10 mm) are made in the patient‘s abdomen through which special viewing and surgical instruments
are passed through to perform the surgery. Compared to conventional surgery, patients who undergo laparoscopy surgery can have reduced
hospital stays, less post-operative pain and side-effects, and better cosmetic results.
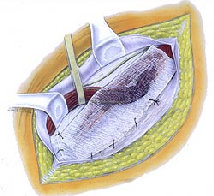
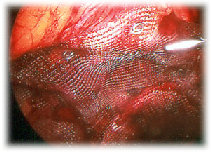
The muscle defect is revealed and the sac of the inguinal hernia is pulled back into this space. A piece of flexible mesh is then slid down the large port and maneuvered so as to cover the hole in the muscle and also all other potential areas where inguinal hernia can occur in this area. The positive pressure in the abdominal cavity pushes the peritoneum onto the mesh trapping it. As the repair is tension free, it is less painful than sutured techniques.
The entire inguinal hernia surgery usually does not take more than 45 minutes and the patient is discharged on the same day with oral pain relief.